Version: 1.1
| Version | Description | Date Updated |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | In-store transactions using QR code is now required | 2024-10-21 |
| 1.0 | Initial version | 2022-03-21 |
This page is specific to Brazilian issuers and highlights the most important local requirements that must be met before launching Google Pay in Brazil. It can also be used to improve existing integrations in order to make the most of Google Pay features.
Local requirements
Card provisioning
Currently, there are two ways of provisioning a card on Google Pay:
Manual Provisioning (MP) refers to tokenizations initiated from the Google Wallet app. Android Push Provisioning (PP) refers to tokenizations that are initiated within the banking app. Further details of both forms will be covered in the next sections.
Transactions
In Brazil, tokenized cards can be used to perform in-store - using NFC and QR code - and e-commerce transactions.
Launch requirements for Brazilian issuers
Below are the current local requirements to launch your Google Pay integration in Brazil:
- Android Push Provisioning is mandatory.
- Manual Provisioning with, at least, one of the following Identity & Verification (ID&V) methods: OTP SMS, OTP Email or App-to-App, is also mandatory.
- Support for in-store - using NFC and QR code - and e-commerce transactions is mandatory:
- In regards to QR code, you must certify your integration with POS terminals from
Cielo,RedeandGetnetthat support credit or debit payments using QR code.
- In regards to QR code, you must certify your integration with POS terminals from
- Meet the exit criteria for both Android Push Provisioning and Manual Provisioning with a special attention to:
- Tokenization success rate of 90%
- Transaction success rate of 90%
- No current issues as depicted in sections MP Common Issues and PP Common Issues
Examples of valid integrations:
- Card provisioning using PP and MP with OTP SMS. Support in-store transactions using NFC and QR code and e-commerce transactions
- Card provisioning using PP and MP with App-to-App. Support in-store transactions using NFC and QR code and e-commerce transactions
- Card provisioning using PP and MP with OTP SMS, Call center. Support in-store transactions using NFC and QR code and e-commerce transactions
Examples of invalid integrations:
- Card provisioning using MP only, with OTP SMS and App-to-App as ID&V methods (PP is missing)
- Card provisioning using PP and MP with Callcenter as ID&V method (OTP SMS, OTP Email or App-to-App is missing)
- Card provisioning using PP only (MP missing)
- Support in-store transactions using NFC only and e-commerce transactions (QR code is missing)
Manual Provisioning (MP)
Manual Provisioning refers to tokenizations that are, normally, initiated from Google Wallet app. The screens below show a common user flow for adding a card to Google Pay:
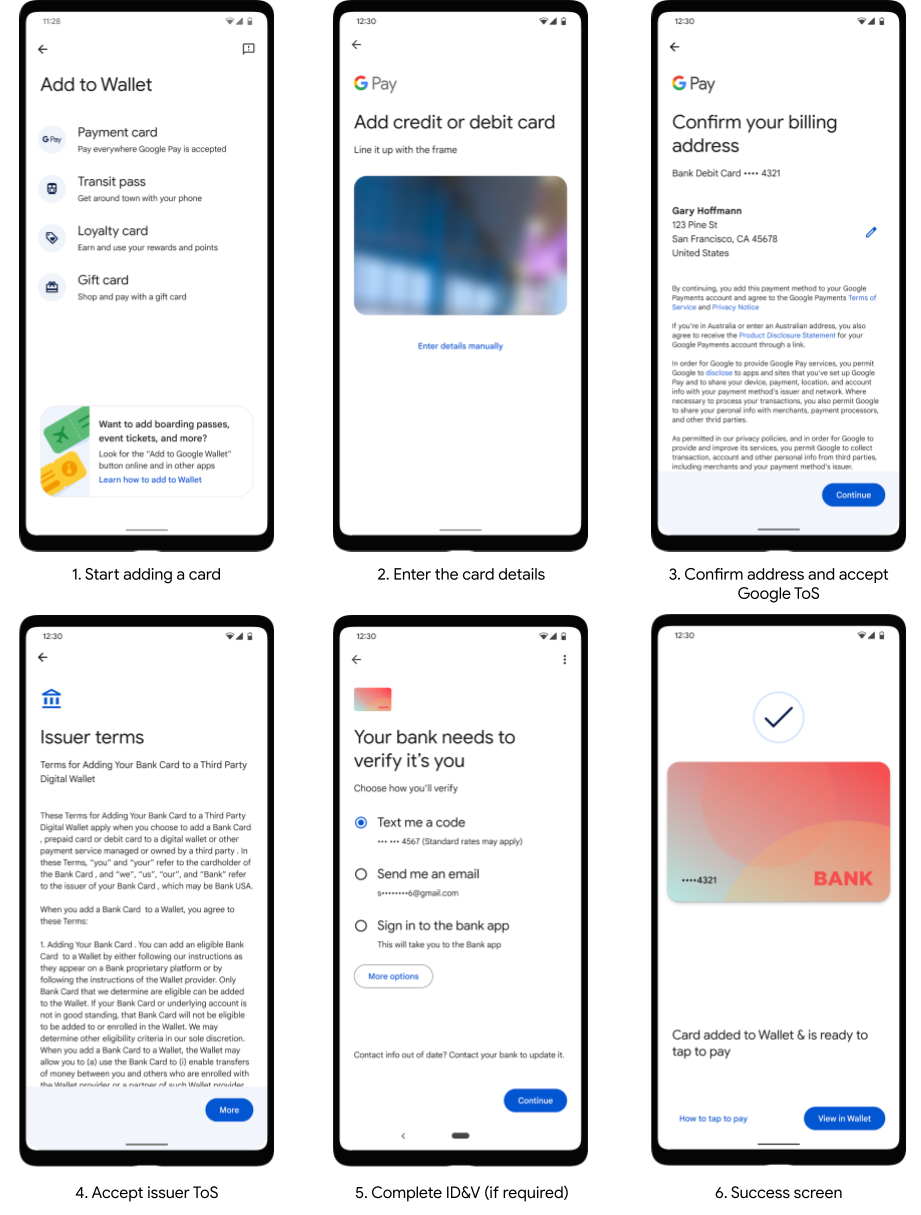
In Brazil it's very common, during the MP tokenization flow, to ask for an extra step of verification (ID&V, shown in screen 5 above), leading to the Yellow authentication path. However, other paths also exist such as Green and Red and, if used wisely, could improve significantly cardholders experience.
Which authentication path should I assign to my cardholder?
Whenever a tokenization takes place, Google Pay will send risk scores to both Network and Issuer. We recommend Issuers to evaluate both Google Pay risk scores along with its internal signals in order to determine which authentication path must be taken. High Google Pay account and device scores, for instance, could lead to the Green path.
If the Yellow authentication path is chosen, a robust Identity & Verification (ID&V) method should be provided and, in Brazil, at least one of the following methods should be implemented: OTP SMS, OTP Email or App-to-App in order to have the launch approved.
Integration process
Below is the integration process for Manual Provisioning. Networks in Brazil are fully capable of guiding Issuers in this type of integration. Reach out to your Network for further details.
| Step | Teams Involved | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Onboard | Issuer & Google | Issuers onboard and sign the NDA / CTA agreements through Issuer Console and obtain access to Issuer documentation. |
| 2. Integrate | Issuer & Network | Networks and Issuers work together to develop two-party integration. Further details in this link. |
| 3. Test | Issuer & Network | Issuers successfully complete all end to end Google Pay test cases, working with Networks as needed. |
| 4. Launch | Issuer & Network | Issuers complete pre-launch requirements, and confirm readiness with Network; Network notifies Google of launch date. Notice that Android Push Provisioning is mandatory in Brazil, therefore this feature must also be implemented before launching. |
MP common issues
Below are the most common issues faced by Issuers during a Manual Provisioning integration:
| Common Issue | Details |
|---|---|
| Not meet the recommended success rates indicated in the exit criteria |
|
| Issuer name in token data incorrect or inconsistent | Issuer names are required to be consistent across all portfolios and Networks and must clearly identify the Issuer by name. ISO Latin characters are preferred but other types are allowed as long as they are consistent. |
| Terms of Service, Privacy Policy and Website link issues | Issuers must use HTTPS links and cannot use links that use Apple Pay/Samsung Pay/other wallets in URL. Issuers may use one page for multiple wallets as long as the page and url do not reference one wallet. |
| Issuer package name missing or incorrect | Issuers with an Android app are expected to set their Android package name to their production app. This is required for Issuers who support App-to-App ID&V. |
Highly recommended links
Android Push Provisioning (PP)
Android Push Provisioning refers to tokenizations that are initiated within the banking app. The screens below illustrate the user flow:

During a PP tokenization, since the cardholder is already within the Issuer app, the provisioning normally goes through the Green authentication path, not requiring, therefore, the Identity & Verification (ID&V) step which leads to a better user experience.
Sample app, API reference and flow diagrams
Google Pay provides a Sample app that can be used, along with the PP API reference and flow diagrams, to have a solid understanding on how to integrate the banking app to PP API. We recommend both UX and developers teams to check the Sample app features and code in order to accelerate the development and launch.
Integration process
Below is the integration process for Android Push Provisioning. Networks in Brazil are fully capable of guiding Issuers in this type of integration. Reach out to your Network for further details.
| Step | Teams Involved | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Onboard | Issuer & Google |
|
| 2. Design | Issuer & Google |
|
| 3. Test | Issuer & Network |
|
| 4. Launch | Issuer & Google |
|
PP common issues
Below are the most common issues faced by Issuers during an Android Push Provisioning integration:
| Common Issue | Details |
|---|---|
| Opaque Payment Card (OPC) Troubleshooting | Google is not able to troubleshoot OPC issues since it's a encrypted object and only Networks know how to build it and are able to decrypt it. Nonetheless, Google Pay provides Issuer developers with a way to capture the error message during a Push Provisioning tokenization. The returned errors message can be sent to the Network POC in order to identify what is wrong. All the steps to check the OPC error can be seen in this link. |
| Not displaying GPay buttons prominently on high-traffic screens | To ensure users see the Google Pay button, add it to screens within your existing user flows. Make sure there is a clear connection between the button and the user’s credit or debit card. Do not display Google Pay buttons on screens that don’t show their cards. |
| Only display Google Pay button if the smartphone has NFC | That's not correct because Google Pay can also be used for secure e-commerce payments. NFC is only required for contactless payments. |
| Banking app not able to resolve "yellow-pathed" tokens leading to errors during tokenization | Details of the scenario and how to handle it in this link. |
| Banking app not always in sync with the wallet | Details of the scenario and how to handle it in this link. |