This overview summarizes the Ordering End-to-End flow and how it interacts with your fulfillment web service.
Ordering
The Ordering End-to-End user interface handles all interactions with the user
as they add menu items to their order and decide on pickup or delivery,
depending on the services offered by the restaurant. This experience is powered
by the Restaurant, Service, and Menu entities found in your
data feeds.
The next step is the cart validation stage where the resulting Cart created
by the user is processed by your web service.
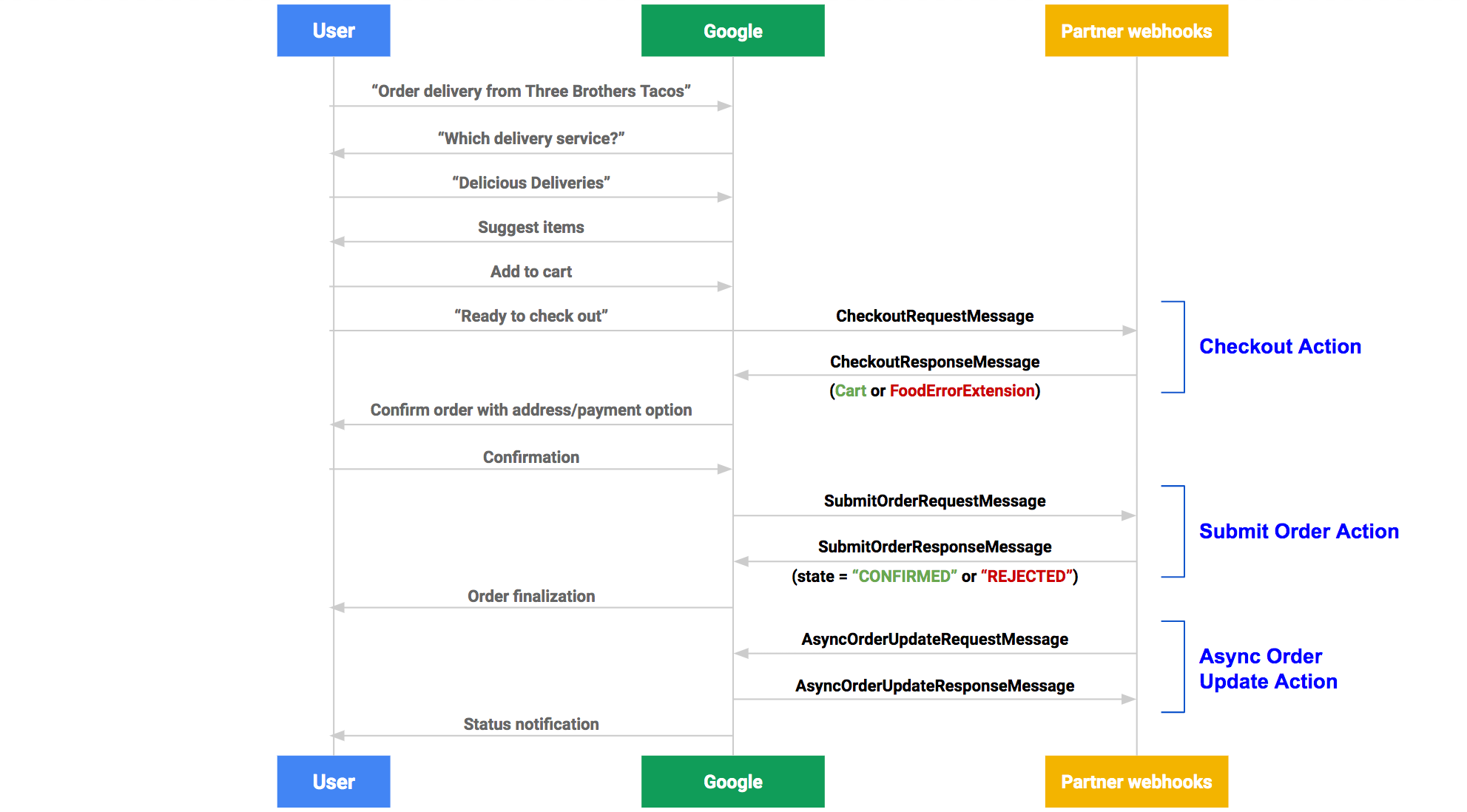
Checkout Action
Checkout action is the first call made by Google to your web service endpoint.
Your web service is responsible for the validation of the Cart. You must
confirm the availability and pricing of items, compute and return taxes,
discounts, and fees, and validate the order delivery address.
The checkout process follows this sequence:
- The Ordering End-to-End service sends a
CheckoutRequestMessagethat contains aCartto your fulfillment web service endpoint. - Your web service needs to validate the items in the
Cartbased on current prices, availability, and service providers. You then calculate the total price, which includes discounts, taxes, and delivery fees. - Your endpoint responds with a
CheckoutResponseMessagethat contains the unmodifiedCartfor successful requests. AFoodErrorExtensioncan be included in theCheckoutResponseMessageto raise a processing error or propose minor changes, if necessary.
After the Cart is validated, the user might choose to proceed to the order
submission stage of the flow.
Submit Order Action
The submit order action is triggered when the user places their order. Your web service must revalidate the cart, process the card token if online payments are enabled, and finally update the status of the order.
The order submission process follows this sequence:
- The Ordering End-to-End service sends a
SubmitOrderRequestMessagethat contains anOrderto your fulfillment web service endpoint. Your backend needs to perform anotherCartvalidation before continuing. Your web service processes the payment details found in the
Order, typically performing the following actions:- Perform token verification, fraud, and other eligibility checks.
- Authorize and, optionally, charge the card.
Your endpoint responds with a
SubmitOrderResponseMessagethat contains anOrderUpdatewith a state ofCREATED("Ordered" purchase status),CONFIRMED("Accepted" purchase status), orREJECTED("Declined" purchase status).
With the order placed, the user expects to receive order status updates from both you and the Ordering End-to-End user interface. You are required to send an order confirmation email to the user. Additionally, you use the Asynchronous Order Update API to send relevant order updates to Google.
Asynchronous Order Update Action
Independent of any user notifications on your end, you must also send order status updates to Google for the following events:
- Changes to
OrderStatesuch as transitions fromCREATEDtoCONFIRMED, andCONFIRMEDtoIN_TRANSIT. - Changes to order items, such as price or availability.
- Whenever the user triggers a support request from one of your customer support channels.
Updates are sent from your web service endpoint as an
AsyncOrderUpdateRequestMessage that contains an OrderUpdate. Google responds
with an AsyncOrderUpdateResponseMessage.
Sequence diagram
The following illustration demonstrates how fulfillment actions interact with your web service. Click to enlarge.

Set up your fulfillment endpoint
The Ordering End-to-End actions use JSON messages to communicate with your web service and handle the processing, confirmation, and updates to food orders. When you design your Ordering End-to-End web service, you must define a URL endpoint that receives request messages from the Ordering End-to-End service and can return messages back to the Google service. Your implementation must meet the following requirements:
- Your web service must be able to receive a JSON message as a
POSTrequest from the Ordering End-to-End service. - Your web service must provide a publicly accessible URL endpoint, called the fulfillment URL, which you specify in the Actions Center. The fulfillment URL is used to check out and submit orders. Your implementation must handle both types of requests.
- Your web service must be able to verify messages from Google using the Message verification method.
- Your implementation of the URL endpoint must be able to handle both checkout and order fulfillment with a single endpoint. You can't have one URL endpoint for checkout and a separate endpoint for ordering submission.
Client Libraries
The client code generator in the Tools section is available to validate your web service against the Fulfillment API specification.