The Maps SDK for iOS offers various ways for you to add shapes to your maps. The following shapes are supported:
- A polyline is a series of connected line segments that can form any shape you want and can be used to mark paths and routes on the map.
- A polygon is an enclosed shape that can be used to mark areas on the map.
- A circle is a geographically accurate projection of a circle on the Earth's surface.
You are able to modify the appearance of each shape in a number of ways.
Polylines
Polylines allow you to draw lines on the map. A GMSPolyline
object represents an ordered sequence of locations, displayed as a series of
line segments. You can set the color of a polyline with
GMSStrokeStyle.
To create a polyline, you'll need to specify its path by creating a
corresponding GMSMutablePath object with two or more points.
Each CLLocationCoordinate2D represents a point on the Earth's surface. Line
segments are drawn between points according to the order in which you add them
to the path. You can add points to the path with the addCoordinate: or
addLatitude:longitude: methods.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath() path.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: -33.85, longitude: 151.20)) path.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: -33.70, longitude: 151.40)) path.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: -33.73, longitude: 151.41)) let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path)
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path]; [path addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.85, 151.20)]; [path addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.70, 151.40)]; [path addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.73, 151.41)]; GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path];
Adding a polyline
- Create a
GMSMutablePathobject. - Set the points in the path with the
addCoordinate:oraddLatitude:longitude:methods. - Instantiate a new
GMSPolylineobject using the path as an argument. - Set other properties, such as
strokeWidthandstrokeColor, as needed. - Set the
mapproperty of theGMSPolyline. - The polyline appears on the map.
The following code snippet adds a rectangle to a map:
Swift
let rectanglePath = GMSMutablePath() rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.0)) rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.45, longitude: -122.0)) rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.45, longitude: -122.2)) rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.2)) rectanglePath.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.0)) let rectangle = GMSPolyline(path: path) rectangle.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *rectanglePath = [GMSMutablePath path]; [rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.0)]; [rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.45, -122.0)]; [rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.45, -122.2)]; [rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.2)]; [rectanglePath addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.0)]; GMSPolyline *rectangle = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path]; rectangle.map = mapView;
Removing a polyline
You can remove a polyline from the map by setting your GMSPolyline's map
property to nil. Alternately, you can remove all of the overlays (including
polylines and other shapes) on the map by calling the GMSMapView
clear method.
Swift
mapView.clear()
Objective-C
[mapView clear];
Customizing a polyline
The GMSPolyline object provides several properties to control
the appearance of the line. It supports the following options:
strokeWidth- The width of the entire line, in screen points. Defaults to 1. The width does not scale when the map is zoomed.
geodesic-
When
YES, render this polyline edge as a geodesic. Geodesic segments follow the shortest path along the Earth's surface and may appear as curved lines on a map with a Mercator projection. Non-geodesic segments are drawn as straight lines on the map. Defaults toNO. spans- Used to specify the color of one or more segments of a polyline. The
spans property is an array of
GMSStyleSpanobjects. Setting thespansproperty is the preferred way to change the color of a polyline. strokeColor- A
UIColorobject specifying the color of the polyline. Defaults toblueColor. ThestrokeColorproperty is ignored ifspansis set.
The following snippet adds a thick polyline from Melbourne to Perth, with geodesic interpolation.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath() path.addLatitude(-37.81319, longitude: 144.96298) path.addLatitude(-31.95285, longitude: 115.85734) let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path) polyline.strokeWidth = 10.0 polyline.geodesic = true polyline.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path]; [path addLatitude:-37.81319 longitude:144.96298]; [path addLatitude:-31.95285 longitude:115.85734]; GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path]; polyline.strokeWidth = 10.f; polyline.geodesic = YES; polyline.map = mapView;
To modify a polyline after it has been added to the map, be sure to keep hold of
the GMSPolyline object.
Swift
polyline.strokeColor = .blue
Objective-C
polyline.strokeColor = [UIColor blueColor];
Changing the color of a polyline
Polylines are drawn as a series of segments on the map. You can change the color
of individual segments, or the entire line, with the spans property. While
this property gives you detailed control over the coloring of a polyline,
several conveniences exist that allow you to apply a single style to the entire
line.
The below snippet uses the spanWithColor: method to change the color of the
entire line to red.
Swift
polyline.spans = [GMSStyleSpan(color: .red)]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithColor:[UIColor redColor]]];
Alternately, if you already have access to a GMSStrokeStyle
object, you can use the spanWithStyle: method.
Swift
let solidRed = GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.red) polyline.spans = [GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed)]
Objective-C
GMSStrokeStyle *solidRed = [GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor redColor]]; polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed]];
Prior to version 1.7 of the Maps SDK for iOS, the single property
strokeColor was available to set the entire color of a
GMSPolyline. The spans property takes precedence over
strokeColor.
Swift
polyline.strokeColor = .red
Objective-C
polyline.strokeColor = [UIColor redColor];
Styles
If your app applies the same stroke color several times, you may find it useful
to define a reusable style. Polyline styles are specified using the
GMSStrokeStyle object. A stroke style can be either a solid
color or a gradient from one color to another color. Once you've created a
style, you can apply it to a GMSStyleSpan with the
spanWithStyle: method.
Swift
// Create two styles: one that is solid blue, and one that is a gradient from red to yellow let solidBlue = GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.blue) let solidBlueSpan = GMSStyleSpan(style: solidBlue) let redYellow = GMSStrokeStyle.gradient(from: .red, to: .yellow) let redYellowSpan = GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow)
Objective-C
// Create two styles: one that is solid blue, and one that is a gradient from red to yellow GMSStrokeStyle *solidBlue = [GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor blueColor]]; GMSStyleSpan *solidBlueSpan = [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidBlue]; GMSStrokeStyle *redYellow = [GMSStrokeStyle gradientFromColor:[UIColor redColor] toColor:[UIColor yellowColor]]; GMSStyleSpan *redYellowSpan = [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow];
A span's style will continue until the end of the polyline, or until a new
style is set. You can change the color of the entire line by setting the spans
property of a polyline to a single GMSStyleSpan The example
demonstrates how to apply a gradient across the entire length of the polyline.
Swift
polyline.spans = [GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow)]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow]];
Changing the color of individual line segments
If you'd like to style each segment of your polyline individually, you can do so
by creating an array of GMSStyleSpan objects, and passing this
to the spans property. By default, each item in the array sets the color of
the corresponding line segment. If there are more elements in the array than
segments in the line, the extra elements will be ignored. If there are fewer
elements in the array, the final GMSStyleSpan describes the
color for the remainder of the line.
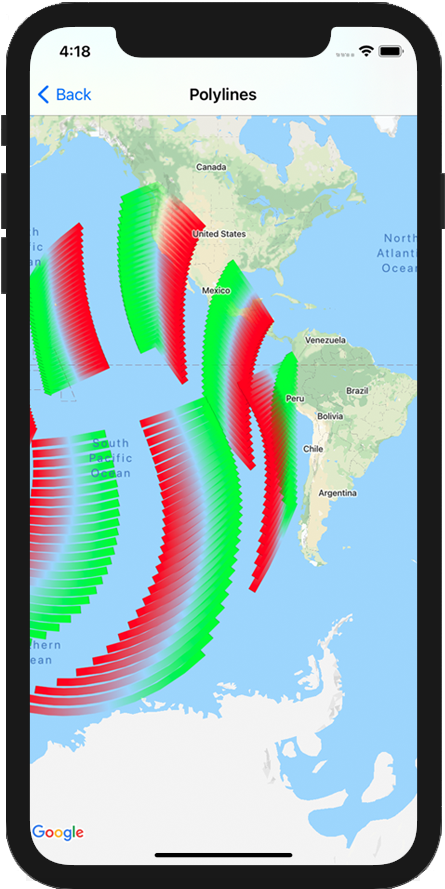
You can use blocks of color and/or gradient polylines to indicate changes along your polyline such as elevation or speed. The below snippet sets the color of the first two segments of a polyline to red, and the remainder of the line is a gradient from red to yellow.
Swift
polyline.spans = [ GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed), GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed), GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow) ]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed], [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed], [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow]];
You can use the spanWithStyle:segments: method to set the style for several
segments at once. For example, the following code is equivalent to the above.
The segment length of the final GMSStyleSpan is always ignored
as the style is used to describe the remainder of the line.
Swift
polyline.spans = [ GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed, segments:2), GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow, segments:10) ]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed segments:2], [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow segments:10]];
Fractional segments
Segments may also be specified as a fractional value. This will apply the style
to the fractional number of segments, potentially causing a split in a single
segment. Each GMSStyleSpan begins immediately after the
previous one: in the example below, the gray color begins from ½ through
the second segment and continue to ½ through the third segment.
Swift
polyline.spans = [ GMSStyleSpan(style: solidRed, segments: 2.5), GMSStyleSpan(color: .gray), GMSStyleSpan(color: .purple, segments: 0.75), GMSStyleSpan(style: redYellow) ]
Objective-C
polyline.spans = @[[GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:solidRed segments:2.5], [GMSStyleSpan spanWithColor:[UIColor grayColor]], [GMSStyleSpan spanWithColor:[UIColor purpleColor] segments:0.75], [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redYellow]];
Adding a repeating color pattern to a polyline
If you'd like to add a pattern to a polyline, you can use the
GMSStyleSpans utility method in GMSGeometryUtils. The
GMSStyleSpans method accepts two arrays that define a repeating pattern. One
array sets the styles that should be repeated, and the other defines the
interval of repetition. Used together you can create a pattern that can be
applied across any polyline, no matter its length or the number of segments
available.
For example, the below code snippet defines a polyline with a black and white
alternating pattern. Its lengths are treated as meters along a rhumb line (in
Mercator, this is a straight line) as the type is specified as
kGMSLengthRhumb.
Swift
let styles = [ GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.white), GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.black) ] let lengths: [NSNumber] = [100000, 50000] polyline.spans = GMSStyleSpans( polyline.path!, styles, lengths, GMSLengthKind.rhumb )
Objective-C
NSArray *styles = @[[GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor whiteColor]], [GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor blackColor]]]; NSArray *lengths = @[@100000, @50000]; polyline.spans = GMSStyleSpans(polyline.path, styles, lengths, kGMSLengthRhumb);
Sprite Stamped Polylines
Sprite Stamped polylines allow you to create a polyline using a repeating bitmap image of your choice. Shapes show with a clear background stroke, but the stamp is not truncated around line corners - making them useful for situations such as dots for illustrating walking directions.
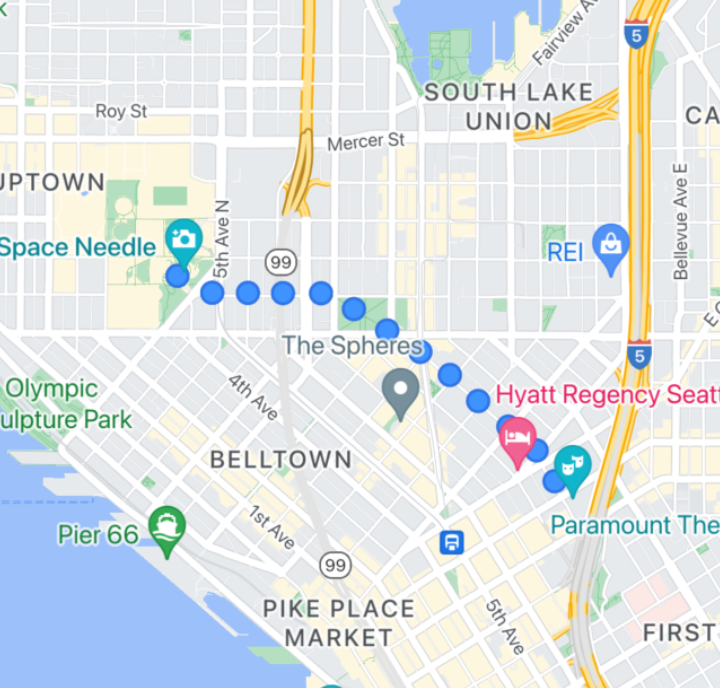
You can use this feature using GMSSpriteStyle and setting it
as the stamp using the GMSStrokeStyle's stampStyle
property.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath() path.addLatitude(-37.81319, longitude: 144.96298) path.addLatitude(-31.95285, longitude: 115.85734) let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path) polyline.strokeWidth = 20 let image = UIImage(named: "imageFromBundleOrAsset")! // Image could be from anywhere let stampStyle = GMSSpriteStyle(image: image) let transparentStampStroke = GMSStrokeStyle.transparentStroke(withStamp: stampStyle) let span = GMSStyleSpan(style: transparentStampStroke) polyline.spans = [span] polyline.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path]; [path addLatitude:-37.81319 longitude:144.96298]; [path addLatitude:-31.95285 longitude:115.85734]; polyline.strokeWidth = 20; GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path]; UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"imageFromBundleOrAsset"]; GMSStrokeStyle *transparentStampStroke = [GMSStrokeStyle transparentStrokeWithStampStyle:[GMSSpriteStyle spriteStyleWithImage:image]]; GMSStyleSpan *span = [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:transparentStampStroke]; polyline.spans = @[span]; polyline.map = _mapView;
Texture Stamped Polylines
Texture stamped polylines allow you to create a polyline using a repeated texture of your choice. Shapes can be shown with clear, solid color or gradient background stroke. The texture resizes as zoom levels change. Images at the end of end or beginning of paths or path points are truncated at certain zoom levels.
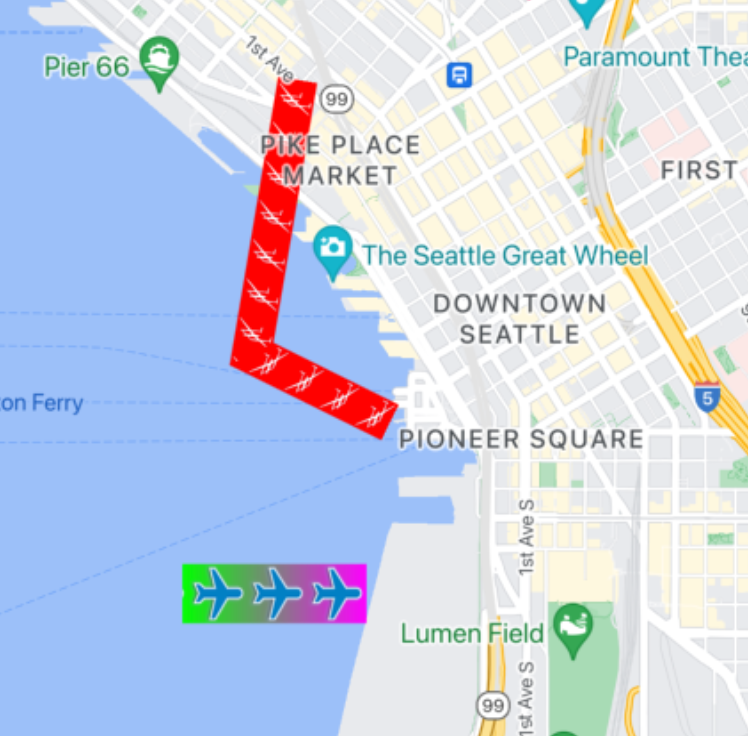
You can use this feature using GMSTextureStyle and setting
it as the stamp using the GMSStrokeStyle's stampStyle
property.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath() path.addLatitude(-37.81319, longitude: 144.96298) path.addLatitude(-31.95285, longitude: 115.85734) let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path) polyline.strokeWidth = 20 let redWithStamp = GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.red) let image = UIImage(named: "imageFromBundleOrAsset")! // Image could be from anywhere redWithStamp.stampStyle = GMSTextureStyle(image: image) let span = GMSStyleSpan(style: redWithStamp) polyline.spans = [span] polyline.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path]; [path addLatitude:-37.81319 longitude:144.96298]; [path addLatitude:-31.95285 longitude:115.85734]; GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path]; polyline.strokeWidth = 20; GMSStrokeStyle *redWithStamp = [GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:[UIColor redColor]]; UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"imageFromBundleOrAsset"]; // Image could be from anywhere redWithStamp.stampStyle = [GMSTextureStyle textureStyleWithImage:image]; GMSStyleSpan *span = [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:redWithStamp]; polyline.spans = @[span]; polyline.map = _mapView;
Map Capabilities
The mapCapabilities property on GMSMapView adds programmatic
checking for map-specific features. This is useful when wanting to know if
certain map capabilities are available before calling specific APIs. This
query determines if the map view supports Sprite Stamped Polylines.
Swift
let path = GMSMutablePath() path.addLatitude(-37.81319, longitude: 144.96298) path.addLatitude(-31.95285, longitude: 115.85734) let polyline = GMSPolyline(path: path) polyline.strokeWidth = 20 let image = UIImage(named: "imageFromBundleOrAsset")! // Image could be from anywhere let spans: [GMSStyleSpan] if (mapView.mapCapabilities.contains(.spritePolylines)) { let spriteStyle = GMSSpriteStyle(image: image) let stroke = GMSStrokeStyle.transparentStroke(withStamp: spriteStyle) spans = [ GMSStyleSpan(style: stroke) ] } else { let stroke = GMSStrokeStyle.solidColor(.clear) stroke.stampStyle = GMSTextureStyle(image: image) spans = [ GMSStyleSpan(style: stroke) ] } polyline.spans = spans polyline.map = mapView
Objective-C
GMSMutablePath *path = [GMSMutablePath path]; [path addLatitude:-37.81319 longitude:144.96298]; [path addLatitude:-31.95285 longitude:115.85734]; UIImage *_Nonnull image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"imageFromBundleOrAsset"]; // Image could be from anywhere NSArray<GMSStyleSpan *> * spans; if (_mapView.mapCapabilities & GMSMapCapabilityFlagsSpritePolylines) { GMSSpriteStyle *spriteStyle = [GMSSpriteStyle spriteStyleWithImage:image]; GMSStrokeStyle *stroke = [GMSStrokeStyle transparentStrokeWithStampStyle:spriteStyle]; spans = @[ [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:stroke] ]; } else { GMSStrokeStyle *stroke = [GMSStrokeStyle solidColor:UIColor.clearColor]; stroke.stampStyle = [GMSTextureStyle textureStyleWithImage:image]; spans = @[ [GMSStyleSpan spanWithStyle:stroke] ]; } GMSPolyline *polyline = [GMSPolyline polylineWithPath:path]; polyline.strokeWidth = 20; polyline.spans = spans; polyline.map = _mapView;
This pattern lets you to subscribe to changes and react to updates with your map
view state. You can also implement didChangeMapCapabilities on
GMSMapViewDelegate to get updates on feature
availability.
Polygons
Polygons are similar to polylines in that they consist of a series of
coordinates in an ordered sequence. However, instead of being open-ended,
polygons are designed to define solid regions within a closed loop. Polygons are
defined in the Maps SDK for iOS by the GMSPolygon
class.
You can add a GMSPolygon to the map in the same way as you add a
GMSPolyline. First, specify its path by creating a
corresponding GMSMutablePath object and adding points to it.
These points form the outline of the polygon. Each CLLocationCoordinate2D
represents a point on the Earth's surface. Line segments are drawn between
points according to the order in which you add them to the path.
Add a polygon
- Create a
GMSMutablePathobject. - Set the points in the path with the
addCoordinate:oraddLatitude:longitude:methods. These points form the outline of the polygon. - Instantiate a new
GMSPolygonobject using the path as an argument. - Set other properties, such as
strokeWidth,strokeColorandfillColor, as desired. - Assign the polygon to a
GMSMapViewobject by setting theGMSPolygon.mapproperty. - The polygon appears on the map.
The following code snippet adds a rectangle to a map.
Swift
// Create a rectangular path let rect = GMSMutablePath() rect.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.0)) rect.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.45, longitude: -122.0)) rect.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.45, longitude: -122.2)) rect.add(CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.36, longitude: -122.2)) // Create the polygon, and assign it to the map. let polygon = GMSPolygon(path: rect) polygon.fillColor = UIColor(red: 0.25, green: 0, blue: 0, alpha: 0.05); polygon.strokeColor = .black polygon.strokeWidth = 2 polygon.map = mapView
Objective-C
// Create a rectangular path GMSMutablePath *rect = [GMSMutablePath path]; [rect addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.0)]; [rect addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.45, -122.0)]; [rect addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.45, -122.2)]; [rect addCoordinate:CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.36, -122.2)]; // Create the polygon, and assign it to the map. GMSPolygon *polygon = [GMSPolygon polygonWithPath:rect]; polygon.fillColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.25 green:0 blue:0 alpha:0.05]; polygon.strokeColor = [UIColor blackColor]; polygon.strokeWidth = 2; polygon.map = mapView;
You can customize the appearance of the polygon both before adding it to the map and after it has been added to the map.
Removing a polygon
Remove a Polygon by setting its GMSPolygon.map property to nil and detaching
the layer from its parent.
Swift
polygon.map = nil polygon.layer.removeFromSuperLayer()
Objective-C
polygon.map = nil; [polygon.layer removeFromSuperlayer];
Circles
In addition to the generic GMSPolygon class, the
Maps SDK for iOS also includes GMSCircle, allowing you
to draw circles on the earth's surface.
To construct a circle, you must specify the following two properties:
positionas aCLLocationCoordinate2D.radiusin meters.
A circle is then defined to be the set of all points on the Earth's surface
which are radius meters away from the given center. Because of how the
Mercator projection used by the Maps API renders a sphere on a flat surface,
this appears as an almost perfect circle on the map when located near the
equator, and appears increasingly non-circular (on the screen) as the circle
moves away from the equator.
Adding a circle
The following code snippet adds a circle to the map:
Swift
let circleCenter = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.35, longitude: -122.0) let circle = GMSCircle(position: circleCenter, radius: 1000) circle.map = mapView
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D circleCenter = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.35, -122.0); GMSCircle *circle = [GMSCircle circleWithPosition:circleCenter radius:1000]; circle.map = mapView;
You can customize the appearance of the circle both before adding it to the map and after it has been added to the map.
Customizing a circle
You can specify custom colors and stroke widths by modifying properties of
GMSCircle. It supports the following options:
fillColor- A
UIColorobject specifying the interior color of the circle. Defaults to transparent. strokeColor- A
UIColorobject specifying the color of the circle's outline. Defaults toblackColor. strokeWidth- The thickness of the circle's outline, in screen points. Defaults to 1. The thickness does not scale when the map is zoomed.
The following snippet adds a thick red circle with a semi-transparent red interior.
Swift
circle.fillColor = UIColor(red: 0.35, green: 0, blue: 0, alpha: 0.05) circle.strokeColor = .red circle.strokeWidth = 5
Objective-C
circle.fillColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.25 green:0 blue:0 alpha:0.05]; circle.strokeColor = [UIColor redColor]; circle.strokeWidth = 5;
Creating a hollow polygon
You can combine multiple paths in a single GMSPolygon object to
create complex shapes, such as filled rings, or donuts (where polygonal areas
appear inside the polygon as separate shapes). Complex shapes are the
composition of multiple paths.
Create a polygon with a path that specifies the largest area covered by the
polygon. Then specify the holes property of the polygon as an array of one or
more GMSPath objects, which define the holes within the polygon.
If a smaller path is fully enclosed by the larger path, it appears as if a piece of the polygon has been removed.
The following code sample creates a polygon with two holes:
Swift
let hydeParkLocation = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: -33.87344, longitude: 151.21135) let camera = GMSCameraPosition.camera(withTarget: hydeParkLocation, zoom: 16) let mapView = GMSMapView.map(withFrame: .zero, camera: camera) mapView.animate(to: camera) let hydePark = "tpwmEkd|y[QVe@Pk@BsHe@mGc@iNaAKMaBIYIq@qAMo@Eo@@[Fe@DoALu@HUb@c@XUZS^ELGxOhAd@@ZB`@J^BhFRlBN\\BZ@`AFrATAJAR?rAE\\C~BIpD" let archibaldFountain = "tlvmEqq|y[NNCXSJQOB[TI" let reflectionPool = "bewmEwk|y[Dm@zAPEj@{AO" let hollowPolygon = GMSPolygon() hollowPolygon.path = GMSPath(fromEncodedPath: hydePark) hollowPolygon.holes = [GMSPath(fromEncodedPath: archibaldFountain)!, GMSPath(fromEncodedPath: reflectionPool)!] hollowPolygon.fillColor = UIColor(red: 1.0, green: 0.0, blue: 0.0, alpha: 0.2) hollowPolygon.strokeColor = UIColor(red: 1.0, green: 0.0, blue: 0.0, alpha: 1.0) hollowPolygon.strokeWidth = 2 hollowPolygon.map = mapView
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D hydeParkLocation = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(-33.87344, 151.21135); GMSCameraPosition *camera = [GMSCameraPosition cameraWithTarget:hydeParkLocation zoom:16]; mapView = [GMSMapView mapWithFrame:CGRectZero camera:camera]; NSString *hydePark = @"tpwmEkd|y[QVe@Pk@BsHe@mGc@iNaAKMaBIYIq@qAMo@Eo@@[Fe@DoALu@HUb@c@XUZS^ELGxOhAd@@ZB`@J^BhFRlBN\\BZ@`AFrATAJAR?rAE\\C~BIpD"; NSString *archibaldFountain = @"tlvmEqq|y[NNCXSJQOB[TI"; NSString *reflectionPool = @"bewmEwk|y[Dm@zAPEj@{AO"; GMSPolygon *hollowPolygon = [[GMSPolygon alloc] init]; hollowPolygon.path = [GMSPath pathFromEncodedPath:hydePark]; hollowPolygon.holes = @[[GMSPath pathFromEncodedPath:archibaldFountain], [GMSPath pathFromEncodedPath:reflectionPool]]; hollowPolygon.fillColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:1.0 green:0.0 blue:0.0 alpha:0.2]; hollowPolygon.strokeColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:1.0 green:0.0 blue:0.0 alpha:1.0]; hollowPolygon.strokeWidth = 2; hollowPolygon.map = mapView;
